Laser machine lens
fiber laser machine lens
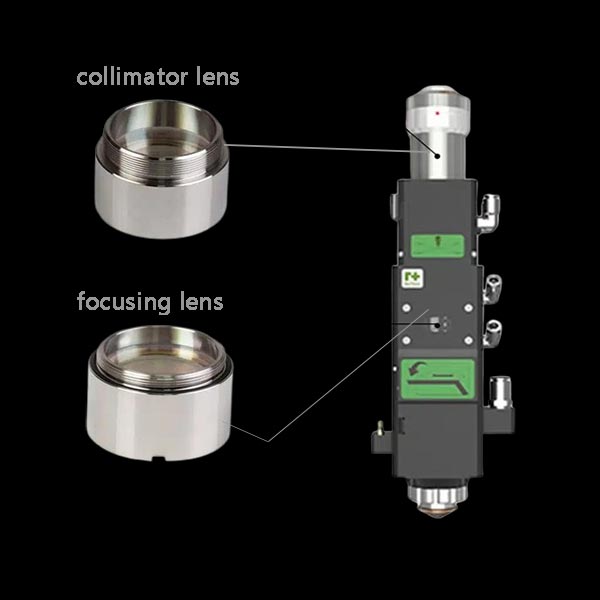
A fiber laser machine lens is the heart of the optical path and determines how the beam is delivered to the workpiece. At the 1064 nm wavelength used by fiber lasers, lenses are typically made from high-purity fused silica with low loss anti-reflection coatings to maximize transmission and withstand high power. The three optics you’ll encounter inside a typical cutting or marking head are the collimating lens (which turns the diverging beam from the fiber into a parallel beam), the focusing lens (which concentrates that parallel beam to a microscopic spot), and when using scan heads an F-Theta lens (to keep spot size uniform across the field). Common focal lengths for focusing optics are 75, 100, 120, 150, and 200 mm; shorter f improves resolution and speed on thin sheets, while longer f increases depth of focus and process stability on thicker sections.
laser machine lens price
Lens price is driven by several factors:
-
Optical substrate & grade. High-grade fused silica with tight wavefront specs (e.g., λ/10) costs more than standard grades.
-
Coatings. Low-loss AR coatings optimized for 1030–1080 nm and contamination-resistant variants raise cost.
-
Power handling & geometry. Larger diameter, thicker lenses with higher laser-damage thresholds (LDT) are pricier.
-
Brand and head compatibility. Optics matched to specific heads (Raytools, Precitec, WSX, etc.) command a premium.
-
Manufacturing tolerances & QA. Better centration, surface quality, and clean-room packaging increase price.
As a rule of thumb, F-Theta lenses (for galvo systems) sit at the top of the price range, focusing lenses in the middle, and collimating lenses near the focusing-lens range depending on diameter and LDT. Exchange rates, availability, and after sales service also affect the final number, so compare like for like specs across suppliers.
laser cutting machine lens
How to select a lens for cutting:
-
Head compatibility. Match diameter and thickness (e.g., Ø20, Ø25.4, Ø30 mm) to your cutting head and holder.
-
Focal length (f).
-
Shorter f → smaller spot, faster cuts on thin materials; more sensitive to standoff and sheet warp.
-
Longer f → larger depth of focus, better tolerance on thicker stock; kerf is a bit wider.
-
-
Material & thickness. Thin stainless often favors f = 100–125 mm; thicker plate tends toward f = 150–200 mm.
-
Assist gas. Nitrogen for bright edges on stainless; oxygen for thicker carbon steel. Nozzle design and gas pressure strongly influence edge quality.
-
Clean optics & alignment. Any contamination increases absorption, heats the spot, and degrades cut quality
laser cutting machine lens price
For cutting systems, expect your lens budget to be centered on:
-
Focusing lenses (f = 100–200 mm): Mid to upper range; high-power grades and anti-spatter/low-loss coatings cost more.
-
Collimating lenses: Typically similar to, or slightly below, the focusing lens price depending on size and spec.
-
F-Theta lenses (if you use a scan head): Usually the highest ticket due to their complex multi-element design.
Plan a 6–12-month maintenance kit around your process: at least one spare focusing lens, one spare collimator (where practical), plus consumables like nozzles, ceramics, height-sensing tips, and sealing elements. This approach minimizes downtime and makes true operating cost more predictable.


laser machine focus lens
The focus lens converts a parallel beam into a small, high-intensity spot at the work surface. Key engineering notes:
-
Source quality (M²) & wavefront. Cleaner beams focus smaller and cut/mark better.
-
Depth of focus. Increases with f and with larger input-beam diameter; use longer f when parts aren’t perfectly flat or Z motion is less stable.
-
Wavelength compatibility. Fiber-laser lenses designed for ~1064 nm are not interchangeable with CO₂laser lenses (10.6 µm); the substrates and coatings are different (fused silica vs. ZnSe).


laser welding machine focus lens
In fiber-laser welding, the focus spot must be stable and resistant to spatter and plume:
-
Longer focal lengths (e.g., 150–200 mm) are common for better access to the joint and greater depth of focus, especially on robotic cells.
-
Process robustness. Optimize shielding gas angle and flow to keep the keyhole stable and limit spatter deposition.
-
Wobble heads. Coordinate the wobble path (circular/figure-8), amplitude, and frequency with focal length to maintain a consistent molten pool.
-
Wire-feed alignment. If using filler wire, align the beam, wire, and joint so the spot leads the wire correctly.
fiber laser lenses
A quick map of the fiber-laser lens family:
-
Collimating lens: Converts the diverging fiber output to a parallel beam; larger diameters and precise coatings are preferred for high power.
-
Focusing lens: Determines spot size and depth of focus; pick f based on thickness, accuracy, and tolerance to standoff variation.
-
F-Theta lens (for galvo systems): Field-flattening optic that maintains uniform spot size and consistent scaling across the scan field.
Fast buying checklist:
-
Laser wavelength & power?
-
Head model and mechanical envelope?
-
Process (cutting/welding/marking) and materials?
-
Desired focal length and edge quality/speed?
-
Warranty, availability, and lead time?